
Calculating A1c
- A blood sample is collected via the vein by a phlebologist
- The blood sample is spun in a machine and separates the red blood cells from the plasma.
- The percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is glycated or bound to glucose.
Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. When blood sugar levels are elevated, glucose molecules in the bloodstream attach to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. This process is known as glycation. The higher the blood sugar levels over time, the more glucose binds to hemoglobin.
A1c testing
The percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood directly corresponds to the amount of glucose exposure in the bloodstream over the lifespan of red blood cells. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately two to three months, the A1c test provides an average of blood sugar levels during that period.
The A1c test measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood. It is expressed as a percentage of total hemoglobin. For example, an A1c value of 6.5% means that 6.5% of the hemoglobin molecules in the blood have glucose attached to them.
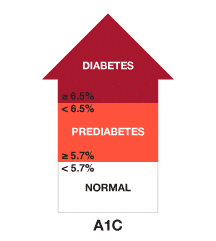
Diagnosing Diabetes with A1c test
Diabetes is diagnosed when the A1c level is 6.5% or higher, prediabetes is diagnosed when the A1c level falls between 5.7% and 6.4%, and a normal A1c level is typically below 5.7%.
A1c testing is recommended every three to six months to monitor their long-term glucose control and assess the effectiveness of their treatment plan. Follow-up testing helps track progress and make any necessary adjustments to optimize diabetes management.
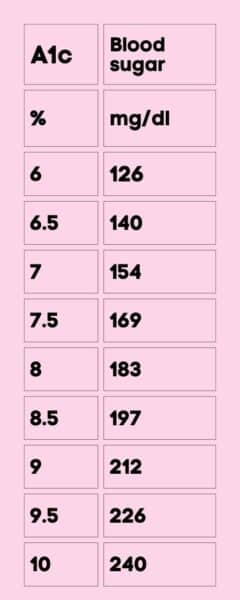
Blood Sugar to A1c Conversion:
The link between A1c and blood sugar is the higher the A1c percentage, the higher the average blood sugar levels over the previous months. For example, an A1c of 6.5% is roughly equivalent to an average blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL. See the blood sugar conversion chart for more information.
The relationship between average blood sugar levels and HbA1c is not linear; a small increase in average blood sugar can result in a larger increase in the HbA1c percentage. Some people with the same A1c may have different blood sugar patterns, and vice versa.

A1c Calculator Considerations:
There are several factors that can also influence the A1c-blood sugar relationship.
-
Red Blood Cell Turnover:
Red blood cells (RBCs) have a lifespan of around 120 days. A1c reflects the average blood sugar levels over this lifespan. If your body has a higher turnover of red blood cells, such as in certain medical conditions or due to medications, it can impact A1c levels.
-
Medical Conditions:
Some medical conditions can affect A1c levels such iron-deficiency anemia, Since this anemia can alter the lifespan of red blood cells, if affects A1c results.
-
Blood Transfusions:
Blood transfusions introduce new red blood cells into your body which can temporarily lower A1c readings.
-
Kidney Function:
Impaired kidney function can affect the lifespan of red blood cells and alter the relationship between blood sugar levels and A1c.
-
Medications:
Some medications such as corticosteroids might affect red blood cell turnover or hemoglobin binding, potentially influencing A1c results.
Summary
Overall, the link between A1c and blood sugar helps guide treatment decisions, set blood sugar targets, and assess the risk of diabetes-related complications, contributing to better overall diabetes care.
If you are looking to lower your A1c I have several resources for you!
I offer 1:1 coaching to get your A1c down and improve diabetes outcomes.
I created a Diabetes Made Easy course which is perfect for the motivated self learner.
I also have a FREE resource for diabetes nutrition.




Pingback: A1c Conversion - Worldnews4
Pingback: A1c Conversion | Dietitian Jess Nutrition - Life's Panorama